Creating a Transformation Graph
This chapter explains the basics of Data Shaper projects and shows you way to create a simple graph that reads records from a CSV file and writes them to a .xlsx file.
Terminology
Before creating a transformation graph we will explain some terms we use in this tutorial.
A workspace is a directory on your computer where your save your projects. It also contains per-workspace configuration. You have chosen it during the start of Designer.
A project is a directory in workspace. It is the location where you place data transformations and data.
A graph , or a transformation graph, is a recipe to data transformation. The graph consists of components which are connected by edges.
Creating a Project
We assume that you have downloaded and installed Data Shaper Designer.
It is the right time to create a new project now.
Select File > New > Data Shaper Project from the main menu.
Type the name of the project, e.g. Project_01.
Creating a New Data File
Now you need a data file. You probably have some. If not, you can create an example file as shown below.
The best practice is to place your input data into data-in.
Right-click data-in item in the Project Explorer pane and select New > File from the context menu.
Type file name, e.g. input.dat. It will be created and stored in the highlighted data-in subfolder.
[block:image] { "images": [ { "image": [ "https://files.readme.io/362a204-DS-CreateNewFile.png", null, "" ], "align": "center", "sizing": "400px", "border": true } ] } [/block]
The file will be created and opened.
Enter some data records in this file; for example, copy and paste the lines below (make sure there is an empty line at the end):
John;Smith;25000
Peter;Brown;30000
George;Hardy;20000
Richard;Gordon;22000
Mark;Taylor;40000
Michael;Lester;18000
George;Smith;30000
Albert;Brown;30000
[block:image] { "images": [ { "image": [ "https://files.readme.io/4873af9-DS-Inputdat.png", null, "" ], "align": "center", "border": true } ] } [/block]
Now you will create your graph.
Creating a Graph
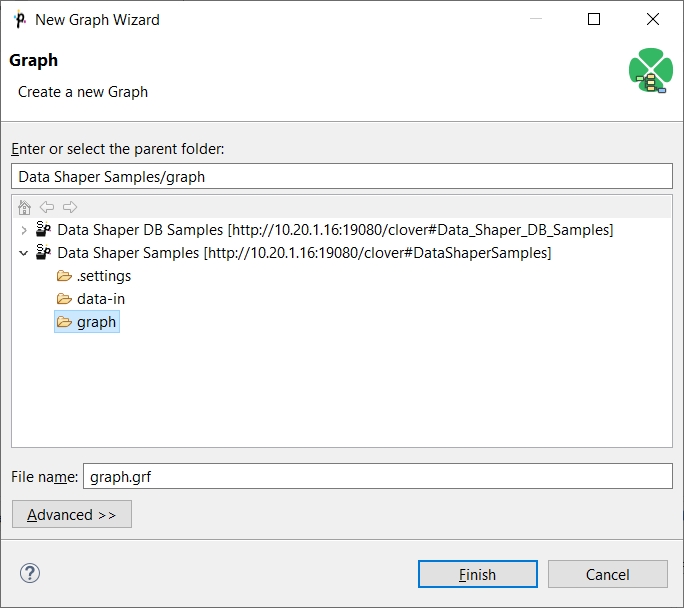
After creating a new project, create a new graph: select File > New > Graph from the main menu. The graph is a recipe of your data transformation.
Give a name to the graph and choose a directory for it. We choose graph as the graph name. Data Shaper Designer gives it the .grf extension automatically.
Data Shaper Designer offers the graph subfolder. It is the recommended place for graphs.
Placing Components in the Graph Editor Pane
To create a graph, select the components from the Palette of Components and place them in the Graph Editor pane. The Palette of Components is located on the right side of the Graph Editor pane.
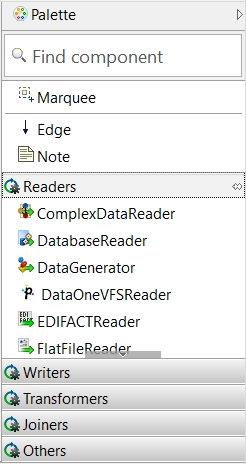
If the Palette is not displayed, click an arrow at the right top of the Graph Editor pane. In this way, the Palette will remain opened until you fold it.
In the Palette, find the FlatFileReader label among Readers. Drag FlatFileReader from the Palette into the Graph Editor pane.
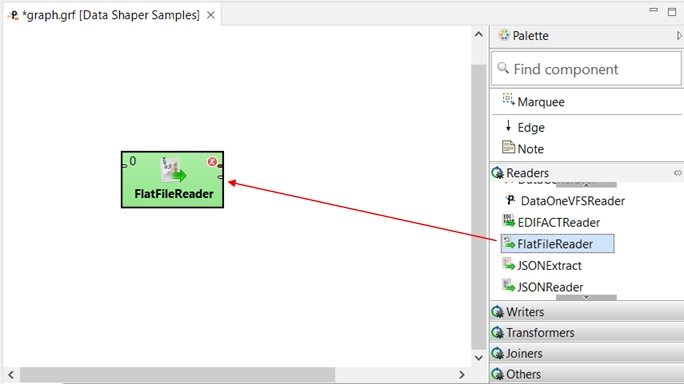
Do the same with the SpreadsheetDataWriter component from Writers. Put these components in the Graph Editor from left to right.
If you know the component name, you can add component using the Add Component dialog window. Press Shift+Space within graph editor and start typing the name.
Connecting Components by an Edge
Click the first output port of FlatFileReader.

An edge appears connected to the output port of the component. Now click inside the Filter component near its input port.
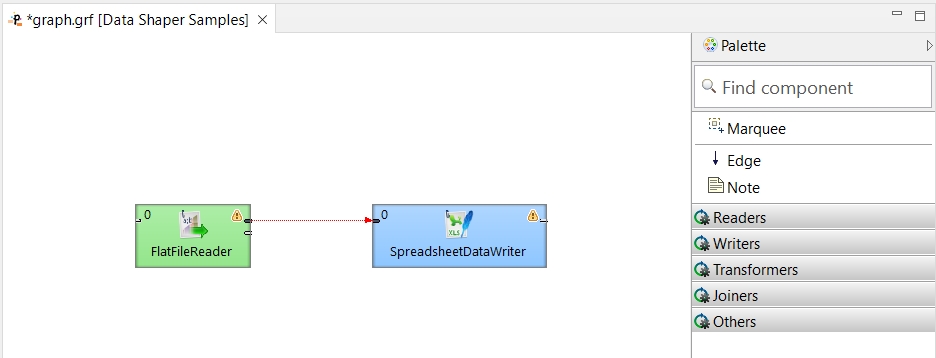
The edges are still red and dashed since no metadata are assigned to them.
If you missed the port, a dialog for adding a new component would appear.
In the next step you will assign metadata to the edge.
Extracting Metadata from the Input File
Metadata is data describing the data structure.
You can extract metadata from your flat data file or create it by your own. To extract it from input file, right-click the first edge and select New metadata > Extract from flat file.
A wizard for metadata extraction opens. Use the Browse button to open the dialog to specify a file.
Select the input.dat file in data-in directory and click the OK button.
The Metadata Editor fills up:
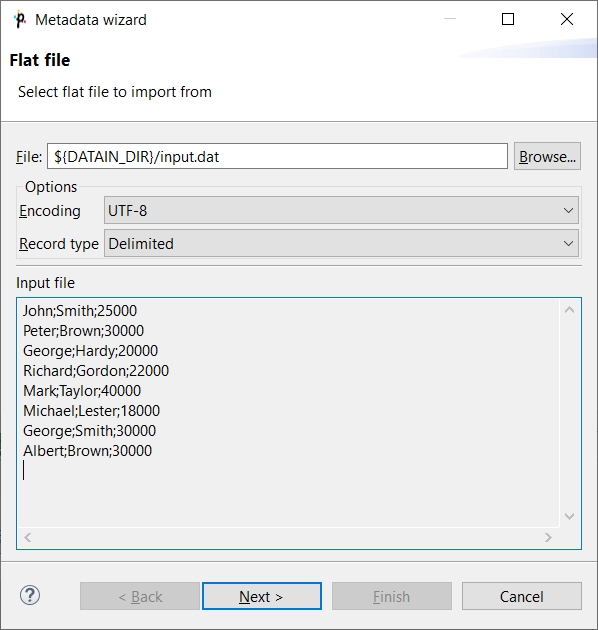
Click Next to specify metadata fields.
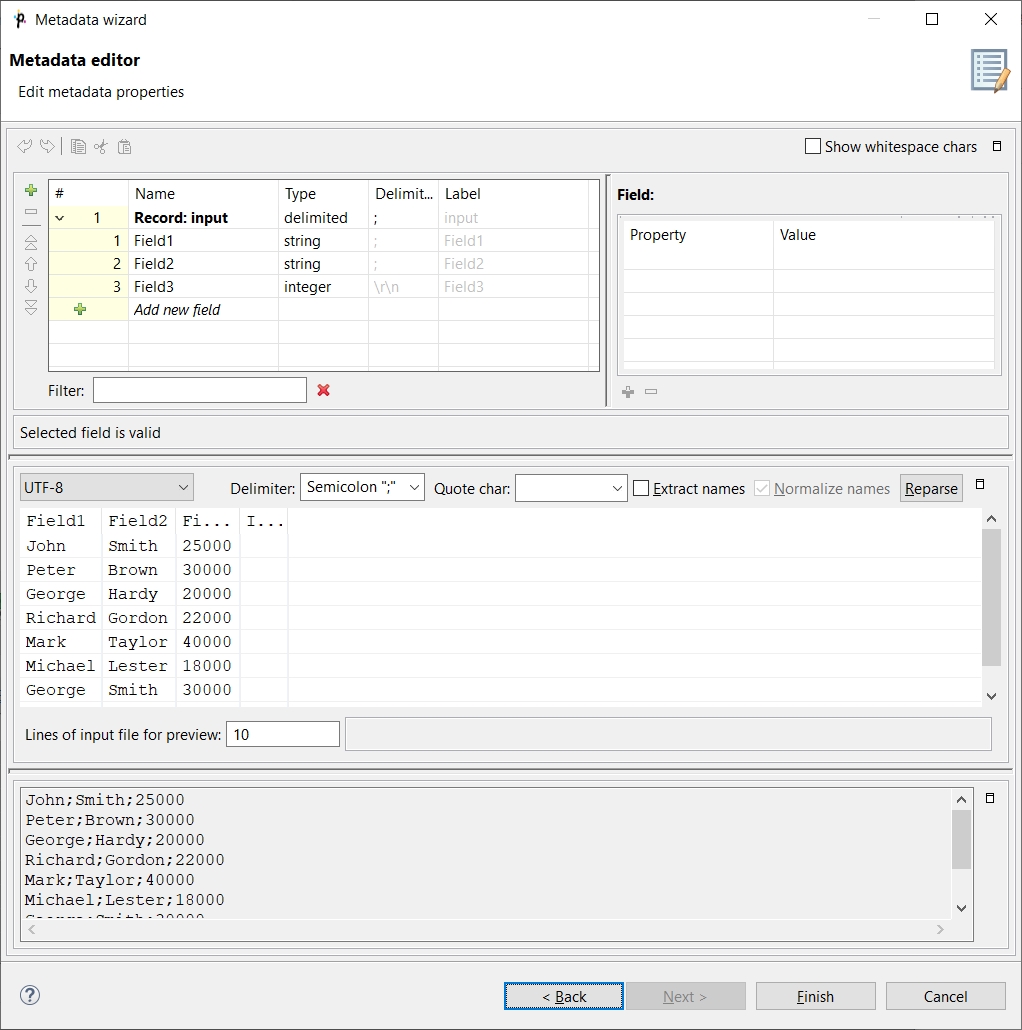
As you can see, the wizard guessed that the records consisted of three fields and it also understood that the third field values were integer numbers.
You can replace the three default field names (Field1, Field2 and Field3) with more descriptive ones: FirstName, LastName and Salary.
To do that, click the Field1 item and enter the new field name.
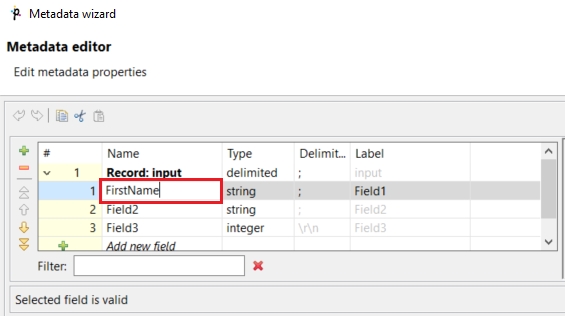
Do the same with the other two field names. The result will look like this:
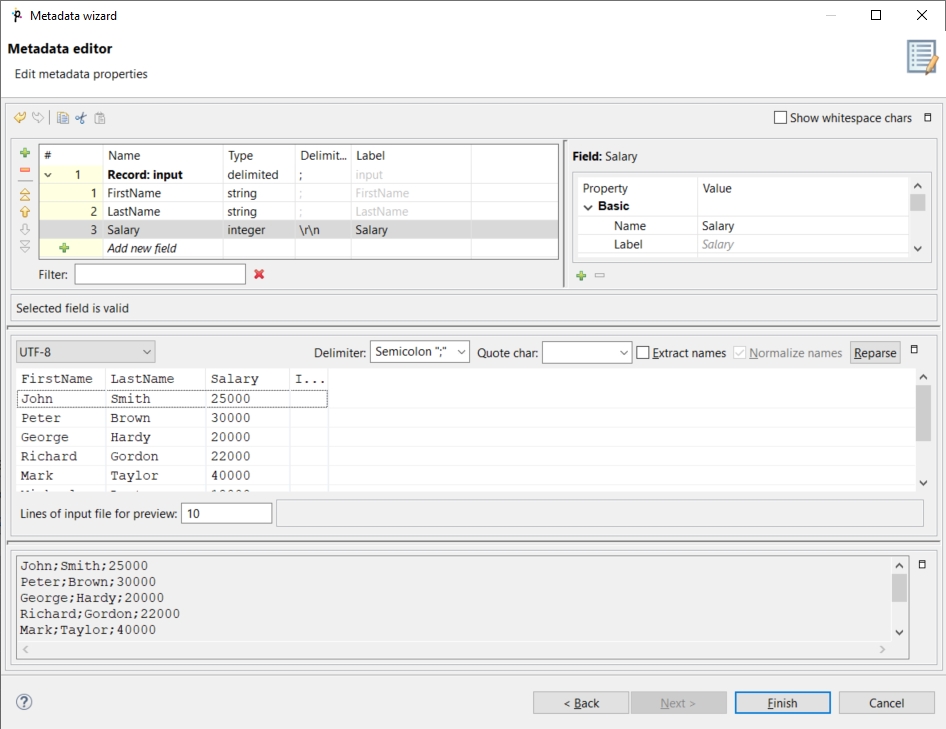
Now click Finish. This way you have created metadata. The metadata has been assigned to the edge.
Assigning Metadata to the Edges
If you have metadata assigned to the edge from previous step, you do not have to assign it once more.
If you have any edge without metadata and you would like to assign the metadata to the edge, right-click the edge and select the Select Metadata item from the context menu.
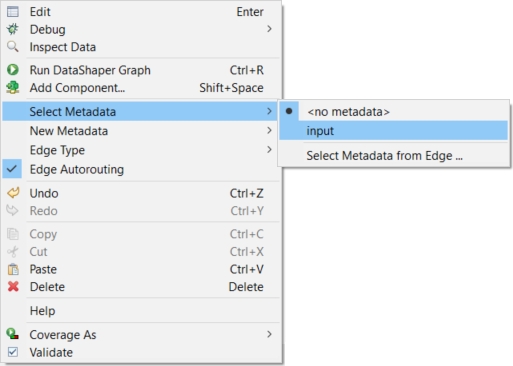
Select the desired metadata by clicking its item. The edge with assigned metadata becomes solid.
Setting Up Readers (FlatFileReader)
To set up the FlatFileReader, double-click this component in the Graph Editor pane. The component editor opens.
Click the File URL attribute row in component editor. A red button appears in the row.
Click the tiny button to open the File URL dialog. The input file is in the data-in directory.
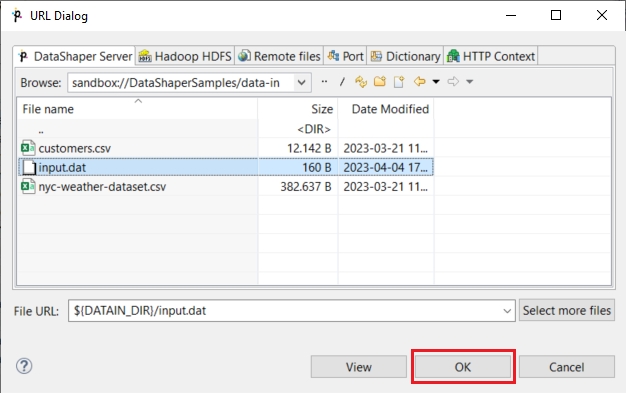
Setting Up Writers (SpreadsheetDataWriter)
When you set up writers, the most important thing is to specify the output files to which data should be written.
Double-click the SpreadsheetDataWriter component. Click the File URL attribute row in the component editor. After that, a button appears in this, click the button.
In the File URL dialog, select the output directory and enter the file name.
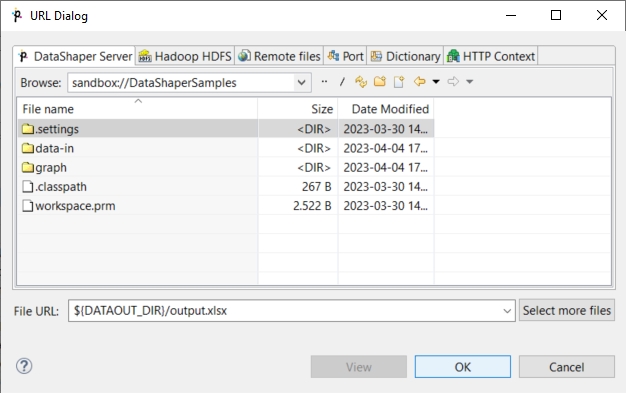
Click OK to use the new component configuration.
You have created a (transformation) graph, use Ctrl-S to save it. The graph is ready to be run.
Running the Graph
To run the graph, right-click anywhere inside the Graph Editor pane and select Run Data Shaper Graph from the context menu. The graph will run.
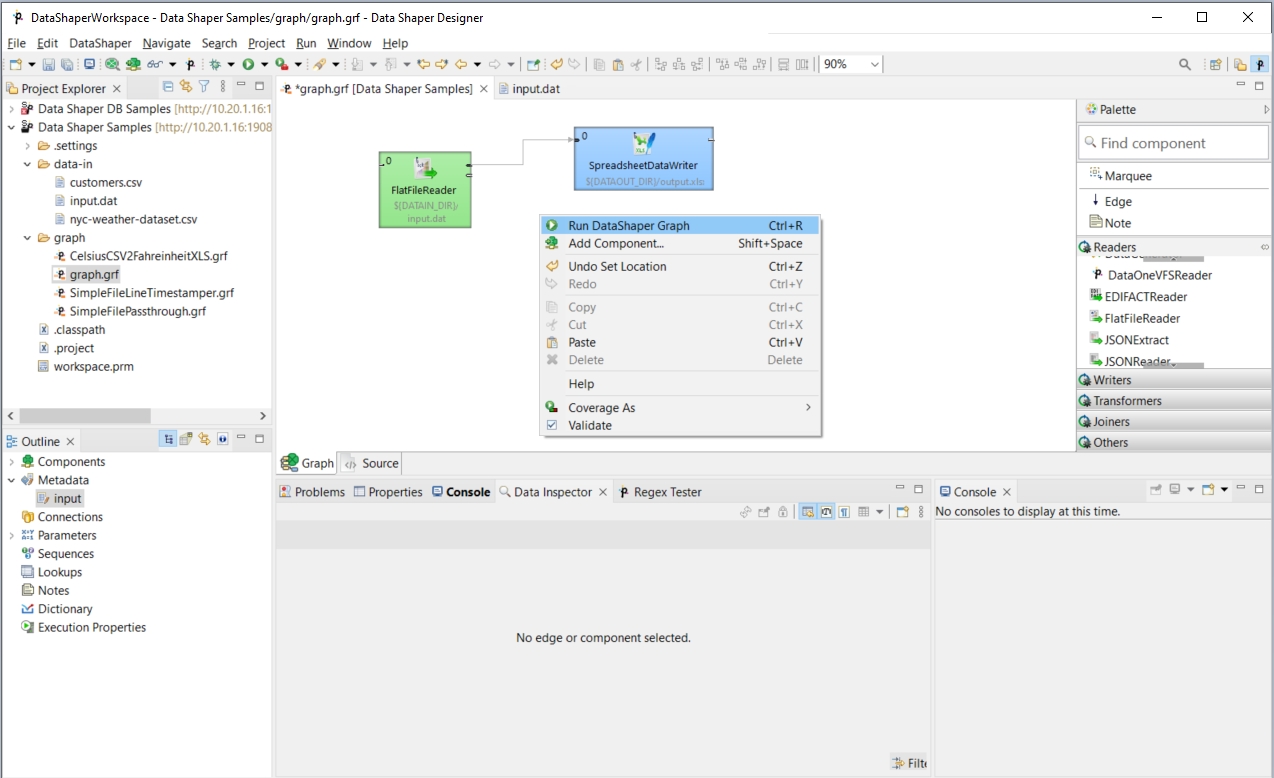
In the Console tab below the Graph Editor pane, you can see the graph run report. If everything is OK, the graph execution will be successful.
You should see the following window with numbers of parsed records near below the edges:
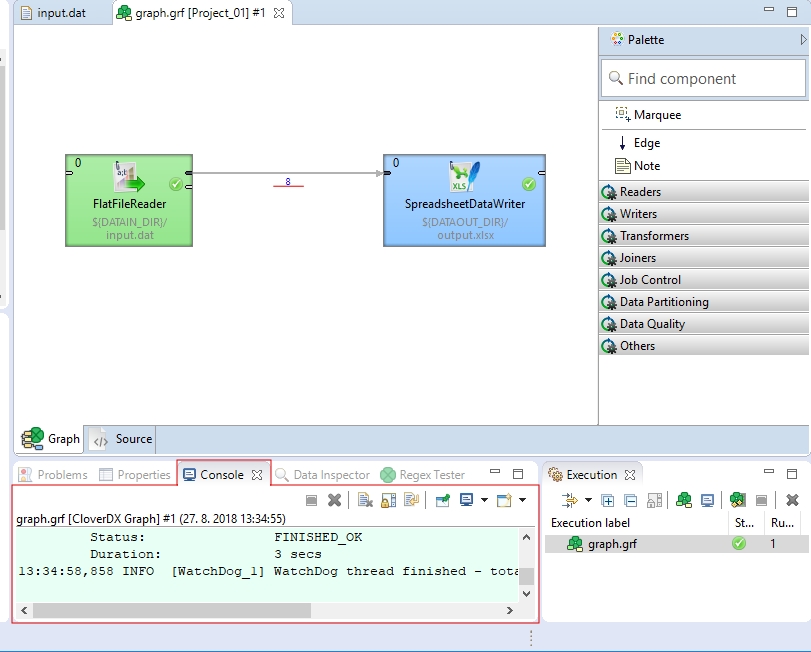
If you would like to see more detailed information about graph run, double-click the Console tab. The tab will cover the whole window. You can restore the original size of this tab when you double-click it again.
Opening the Output File
After running a graph, the file structure of the Project Explorer pane refreshes automatically. Expand the data-out item to see the output.xlsx file.
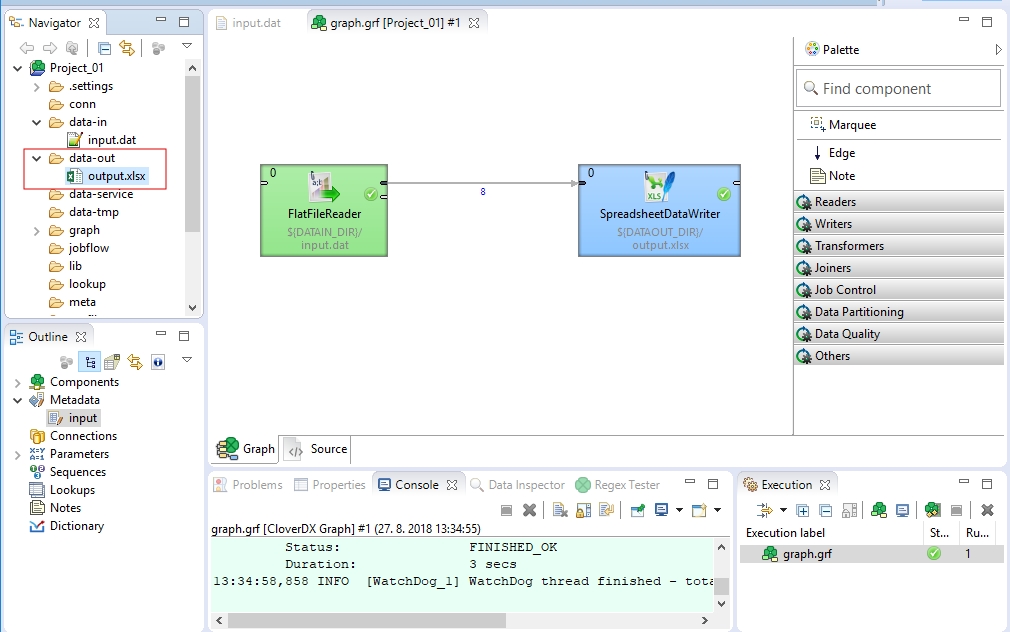
Double click the file to open it with an appropriate spreadsheet editor.
Summary
We have learned to:
create a transformation graph
place component to a graph
assign metadata to an edge
run a graph
read data from a CSV file
write data to Excel spreadsheet
What to do next
You can continue with Filtering the records or Sorting the Records.
You can also play with built-in pre-prepared examples: Help > Data Shaper Examples.
Last updated