Types of Lookup Tables
After opening the New lookup table wizard, you need to select the desired lookup table type.
Simple Lookup Table
Yes
Yes
Database Lookup Table
No
Yes
Range Lookup Table
Yes
No, but intervals may overlap
Persistent Lookup Table
No
Yes
Aspell Lookup Table
Yes
Yes
Simple Lookup Table
All data records stored in simple lookup table are kept in memory. For this reason, to store all data records from the lookup table, sufficient memory must be available. If data records are loaded to a simple lookup table from a data file, the size of the available memory should be approximately at least 6 times bigger than that of the data file. However, this multiplier is different for different types of data records stored in the data file.
Simple lookup table allows storing multiple data records with the same key value. If you do not allow storing duplicated values, the last value will be stored.
Creating Simple Lookup Table
In the first step of the wizard, choose Simple lookup.
In the next step, set up the required properties: in the Table definition tab, give a Name to the lookup table, select the corresponding Metadata and the Key that should be used to look up data records from the table.
Optionally, you can select a Charset and the Initial size of the lookup table (512 by default). You can change the default value by changing the Lookup.LOOKUP_INITIAL_CAPACITY value in defaultProperties.
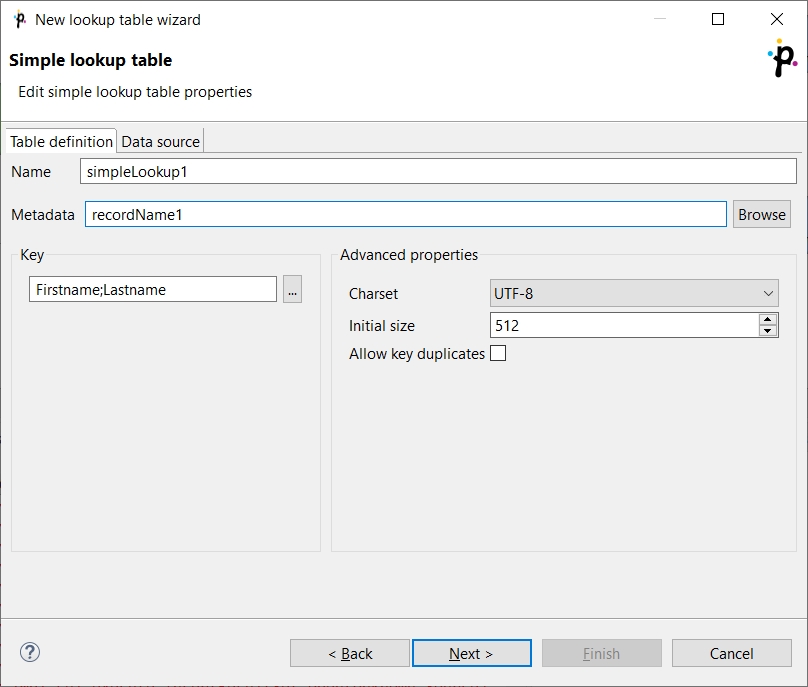
Key
After clicking the button on the right side from the Key area, you will be presented with the Edit key dialog which helps you select the Key. The list on the left side contains metadata fields and their data types. The list on the right side contains metadata fields that form the key.
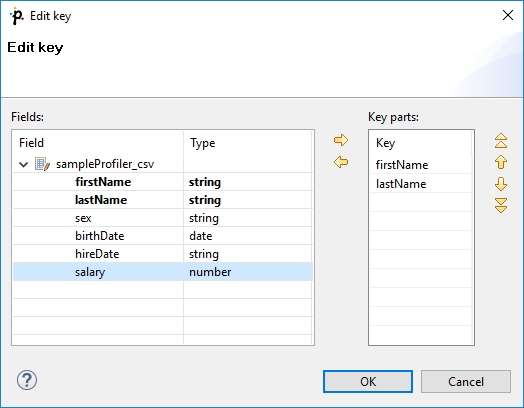
To add a metadata field to the key, drag the field from the list on the left and drop it to the list on the right. Any highlighted metadata field can be added to the list with an arrow too.
You can move the field name(s) into the Key parts pane by highlighting the field name(s) in the Field pane and clicking the Right arrow button. You can keep moving more fields into the Key parts pane.
You can also change the position of any of them in the list of the Key parts by clicking the Up or Down buttons. The key parts that are higher in the list have higher priority. When you have finished, you only need to click OK.
You can also remove any key part by highlighting it and clicking the Left arrow button.
Data Source Tab
In the Data source tab, you can either locate the file URL or fill in the grid after clicking the Edit data button. After clicking OK, the data will appear in the Data text area. If you use LookupTableReaderWriter to fill in the table, you do not need to specify data on the Data source tab.
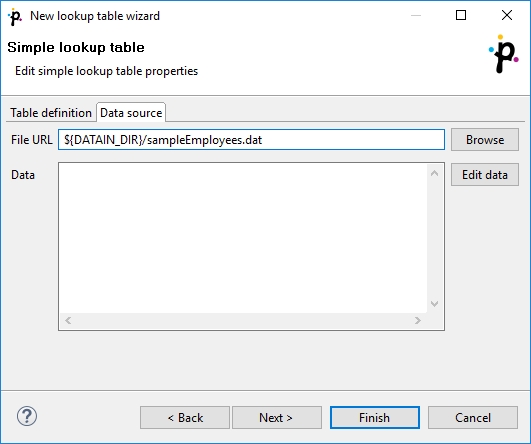
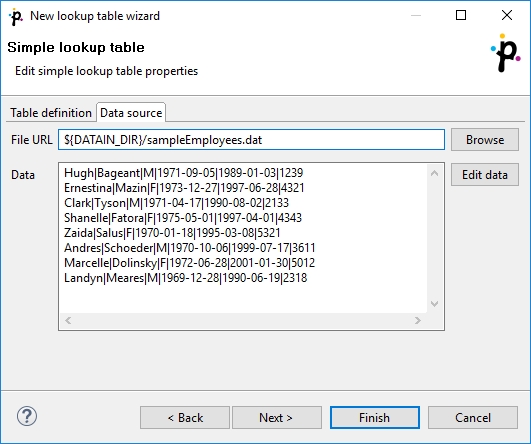
You can set or edit the data after clicking the Edit data button.
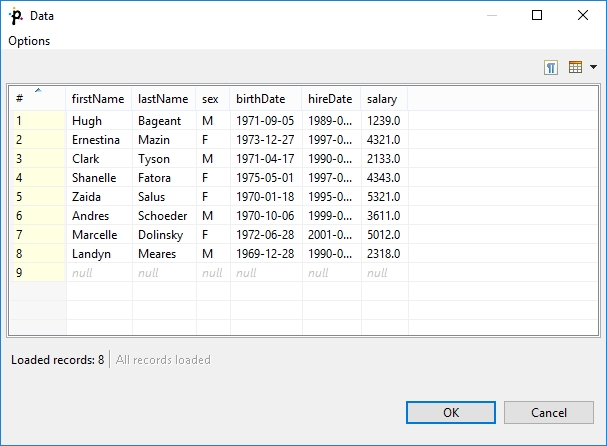
After that, click OK and then Finish.
Simple lookup table is allowed to contain data specified directly in the grid, data in the file or data that can be read using LookupTableReaderWriter.
Database Lookup Table
This type of lookup table works with databases and unloads data from them by using a SQL query. Database lookup table reads data from the specified database table. The key used to search records from this lookup table is the where fieldName = ? [and …] part of the query.
Data records unloaded from the database can be cached in memory keeping the LRU order (the least recently used items are discarded first). To cache them, you must specify the number of such records (Max cached records).
You can cache only the record found in the database, or you can cache both records found as well as records not found in the database. To save both, use Store negative key response checkbox. Then, the lookup table will not search through the database table when the same key value is given again.
Database lookup table allows to work with duplicate records (multiple records with the same key value).
Creating Database Lookup Table
In the first step of the wizard, choose the Database lookup radio button and click Next.
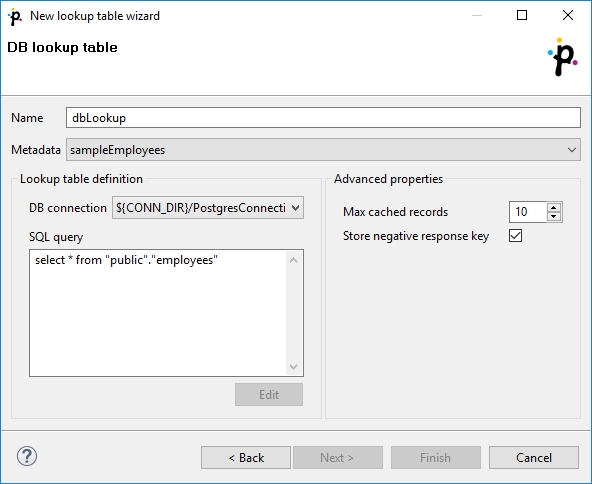
Then, in the Database lookup table wizard, give a Name to the selected lookup table, and specify Metadata and DB connection.
Type or edit a SQL query that serves to look up data records from the database. When you want to edit the query, click the Edit button and, if your database connection is valid and working, you will be presented with the Query wizard, where you can browse the database, generate a query, validate it and view the resulting data.
Warning!
To specify a lookup table key, add a "where fieldName = ? [and …]" statement at the end of the query, fieldName being, for example, "EMPLOYEE_ID". Records matching the given key replace the question mark character in the query.
Then, you can click OK and Finish. See Extracting Metadata from a Database for more details about extracting metadata from a database.
Range Lookup Table
You can create a Range lookup table only if some fields of the records create ranges. That means the fields are of the same data type and they can be assigned both start and end. You can see this in the following example:
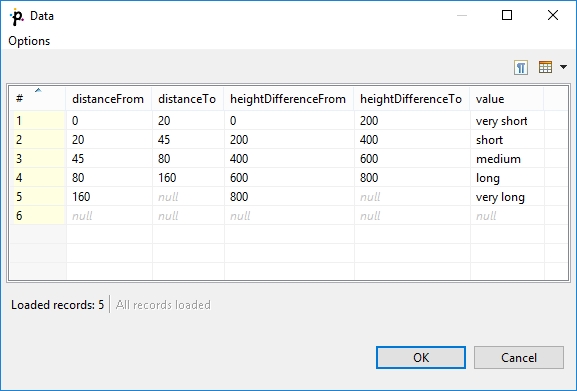
Range lookup table does not allow multiple records with the same interval. The intervals may overlap, therefore one value can match more values from the lookup table.
Creating Range Lookup Table
When you create a Range lookup table, you check the Range lookup radio button and click Next.
Then, in the Range lookup table wizard, give a Name to the selected lookup table, and specify Metadata.
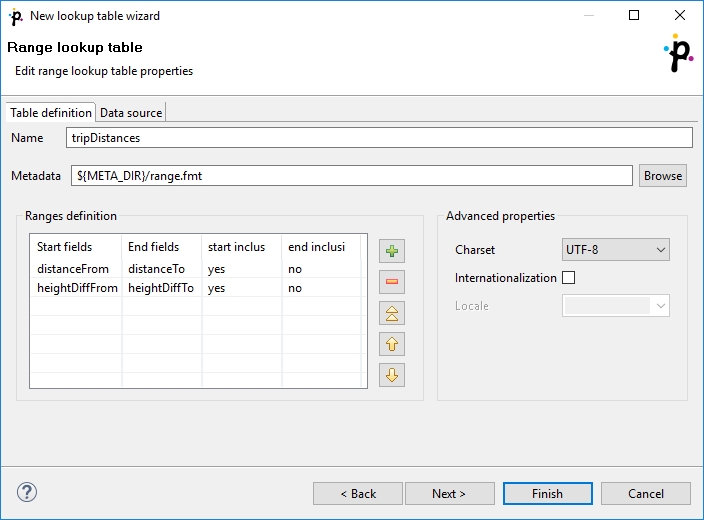
You can select Charset and decide whether Internationalization and what Locale should be used.
By clicking the buttons at the right side, you can add either of the items, or move them up or down.
You must also select whether any start or end field should be included in these ranges or not. You can do it by selecting any of them in the corresponding column of the wizard and clicking.
When you switch to the Data source tab, you can specify the file or directly type the data in the grid. You can also write data to lookup table using LookupTableReaderWriter.
By clicking the Edit button, you can edit the data contained in the lookup table. At the end, you only need to click OK and Finish.
Remember that Range lookup table includes only the first record with identical key value.
There is an example on Range Lookup Table in LookupJoin.
Persistent Lookup Table
This type of lookup table serves a great number of data records. The data records are stored in files; only a few records are cached in main memory. These files are in JDBM format (http://jdbm.sourceforge.net). When you specify the file name, two files will be created: with db and lg extensions.
Persistent lookup table can work in two modes: with key duplicates and without key duplicate. If you switch between the modes, you should delete and refill the lookup table.
Without key duplicates
With the Allow key duplicates property unchecked, the persistent lookup table does not allow storing multiple records with the same key value. You can choose whether to store the first one or the last with the Replace checkbox.
This is the default option.
With key duplicates
With Allow key duplicates property enabled, you can store multiple records with the same key to the table. The Replace property is not used. Key duplicates in persistent lookup table are available since 4.3.0.
Persistent lookup table internally uses B+Tree to store the records. If node is mentioned here, it is the node of the B+Tree.
Creating Persistent Lookup Table
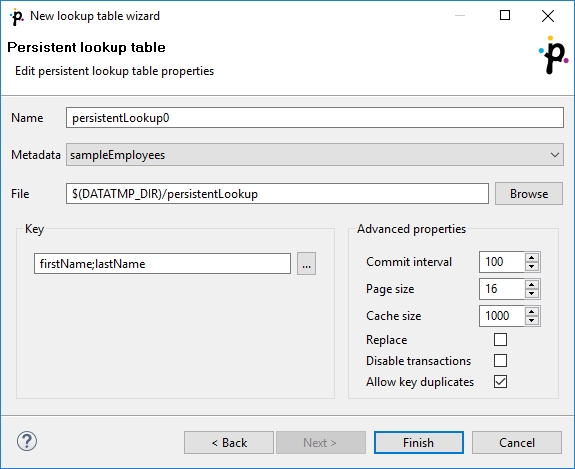
In the first step of the wizard, choose Persistent lookup.
Then set up the required properties: give a Name to the lookup table, select the corresponding Metadata, specify the File where the data records of the lookup table will be stored and the Key that should be used to look up data records from the table.
Advanced Properties
To overwrite old records with newer ones, check the Replace checkbox. This way, the latest record with the same key is stored. Otherwise the first record with the same key would be stored.
You can disable transactions with Disable transactions. Disabling transactions increases graph performance; however, it can cause data loss if manipulation with the table is interrupted.
Commit interval defines the number of records that are committed at once. When the limit or end of phase is reached, the records are committed to the lookup table.
By specifying Page size, you are defining the number of entries (records) per node of B+Tree (in the implementation).
Cache size specifies the maximum number of nodes (of B+Ttree) in cache.
Allow key duplicates allows storing multiple records with the same key value.
Then click OK and Finish.
Using Persistent Lookup Table
You can use LookupTableReaderWriter to add records to Persistent Lookup Table.
Persistent Lookup Table Configuration Tweaks
Performance of persistent lookup table can be affected by the advanced parameters. These parameters configure the internal B+Tree implementation and size of caches.
To speed up reading, increase cache size.
To speed up writing, increase commit interval.
Aspell Lookup Table
All data records stored in this lookup table are kept in memory. For this reason, to store all data records from the lookup table, sufficient memory must be available. If data records are loaded to Aspell lookup table from a data file, the size of available memory should be approximately at least 7 times bigger than that of the data file. However, this multiplier is different for different types of data records stored in the data file.
If you are working with data records that are similar but not fully identical, you should use this type of lookup table. For example, you can use Aspell lookup table for addresses.
Aspell lookup table allows you to have multiple records with the same key value.
Creating Aspell Lookup Table
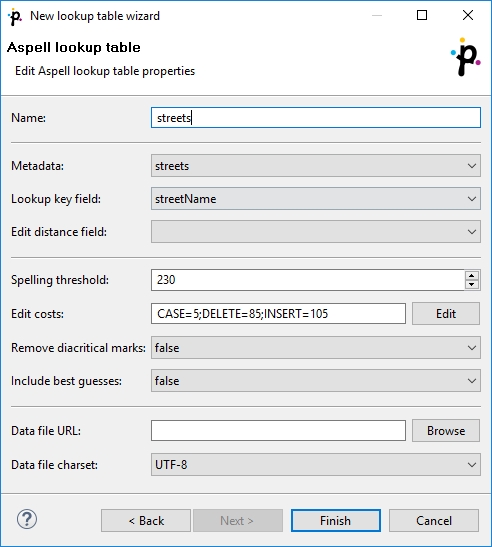
In the Aspell lookup table wizard, you set up the required properties. You must give a Name to the lookup table, select the corresponding Metadata, select the Lookup key field that should be used to look up data records from the table (must be of string data type).
You can also specify the Data file URL where the data records of the lookup table will be stored and the charset of data file (Data file charset). The default charset is UTF-8.
You can set the threshold that should be used by the lookup table (Spelling threshold). It must be higher than 0. The higher the threshold, the more tolerant is the component to spelling errors. Its default value is 230. It is the edit_distance value from the query to the results. Words with this value higher that the specified limit are not included in the results.
You can also change the default costs of individual operations (Edit costs):
Case cost Used when the case of one character is changed.
Transpose cost Used when one character is transposed with another in the string.
Delete cost Used when one character is deleted from the string.
Insert cost Used when one character is inserted to the string.
Replace cost Used when one character is replaced by another one.
You need to decide whether the letters with diacritic marks are considered identical with those without these marks. To do that, you need to set the value of the Remove diacritic marks attribute. If you want diacritic marks to be removed before computing the edit_distance value, you need to set this value to true. This way, letters with diacritic marks are considered equal to their Latin equivalents. (Default value is false. By default, letters with diacritic marks are considered different from those without.)
If you want best guesses to be included in the results, set Include best guesses to true. The default value is false. Best guesses are the words whose edit_distance value is higher than the Spelling threshold, for which there is no other better counterpart.
Then click OK and Finish.
Warning!
If you want to know the distance between the lookup table and edge values, you must add another field of numeric type to lookup table metadata. Set this field to Autofilling (default_value).
Select this field in the Edit distance field combo.
When you are using Aspell lookup table in LookupJoin, you can map this lookup table field to corresponding field on the output port 0.
This way, values that will be stored in the specified Edit distance field of lookup table will be sent to the output to another specified field.
Last updated