DatabaseReader
Short Description
DatabaseReader unloads data from database using JDBC driver. Supports Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Access, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, SQLite, Sybase, Vertica, DB2 and any other database with JDBC compliant driver.
DatabaseReader
database
0-1
1-n
✓
x
x
x
x
x
x
Ports
Input
0-1
x
Incoming queries to be used in the SQL query attribute. When the input port is connected, Query URL should be specified as e.g. port:$0.fieldName:discrete. See Reading from Input Port in Supported File URL Formats for Readers.
Output
0
✓
For correct data records
equal metadata
1-n
x
For correct data records
equal metadata
Metadata
DatabaseReader does not propagate metadata. DatabaseReader has no metadata templates. Output metadata can use Autofilling Functions.
DatabaseReader Attributes
BASIC
DB connection
✓
An ID of a database connection to be used to access the database
SQL query
[bl
The SQL query defined in the graph. For detailed information, see SQL Query Editor below.
Query URL
[bl
The name of an external file, including the path, defining the SQL query.
Query source charset
Encoding of an external file defining the SQL query.
The default encoding depends on DEFAULT_CHARSET_DECODER in defaultProperties.
UTF-8 |
Data policy
Determines what should be done when an error occurs. For more information, see Data Policy.
Strict (default) | Controlled { | Lenient
Print statement
If enabled, SQL statements will be written to the log.
false (default) | true
ADVANCED
Fetch size
Specifies the number of records that should be fetched from the database at once.
20 | 1-N
Incremental file
[bl
The name of the file storing the incremental key, including the path. See Incremental Reading.
Incremental key
[bl
A variable storing the position of the last read record. See Incremental Reading.
Auto commit
By default, your SQL queries are committed immediately. If you need to perform more operations inside one transaction, switch this attribute to false.
true (default) | false
[1] At least one of these attributes must be specified. If both are defined, only Query URL is applied. [2] Controlled data policy in DatabaseReader does not send error records to the edge. Errors are written into the log. [3] Either both or neither of these attributes must be specified.
Details
DatabaseReader unloads data from a database table using an SQL query or by specifying a database table and defining a mapping of database columns to Clover fields. It can send unloaded records to all connected output ports.
Defining Query Attributes
Query Statement without Mapping When the order of Data Shaper metadata fields and database columns in select statement is the same and data types are compatible, implicit mapping can be used which performs positional mapping. A standard SQL query syntax should be used:
select * from table [where dbfieldJ = ? and dbfieldK = somevalue]select column3, column1, column2, … from table [where dbfieldJ = ? and dbfieldK = somevalue]For information about how an SQL query can be defined, see SQL Query Editor.
Query Statement with Mapping If you want to map database fields to Clover fields even for multiple tables, the query will look like this:
select $cloverfieldA:=table1.dbfieldP, $cloverfieldC:=table1.dbfieldS, … , $cloverfieldM:=table2.dbfieldU, $cloverfieldM:=table3.dbfieldV from table1, table2, table3 [where table1.dbfieldJ = ? and table2.dbfieldU = somevalue]For information about how an SQL query can be defined, see SQL Query Editor.
Dollar Sign in DB Table Name
A single dollar sign in a table name must be escaped by another dollar sign; therefore every dollar sign in a database table name will be transformed to a double dollar sign in the generated query. Meaning that each query must contain an even number of dollar signs in the DB table (consisting of adjacent pairs of dollars).
SQL Query Editor
For defining the SQL query attribute, SQL query editor can be used.
The editor opens after clicking the SQL query attribute row:
On the left side, there is the Database schema pane containing information about schemas, tables, columns, and data types of these columns.
Displayed schemas, tables, and columns can be filtered using the values in the ALL combo, Filter in view text area, Filter and Reset buttons, etc.
You can select any columns by expanding schemas, tables and clicking Ctrl+Click on desired columns.
Adjacent columns can also be selected by clicking Shift+Click on the first and the last item.
Then you need to click Generate after which a query will appear in the Query pane.
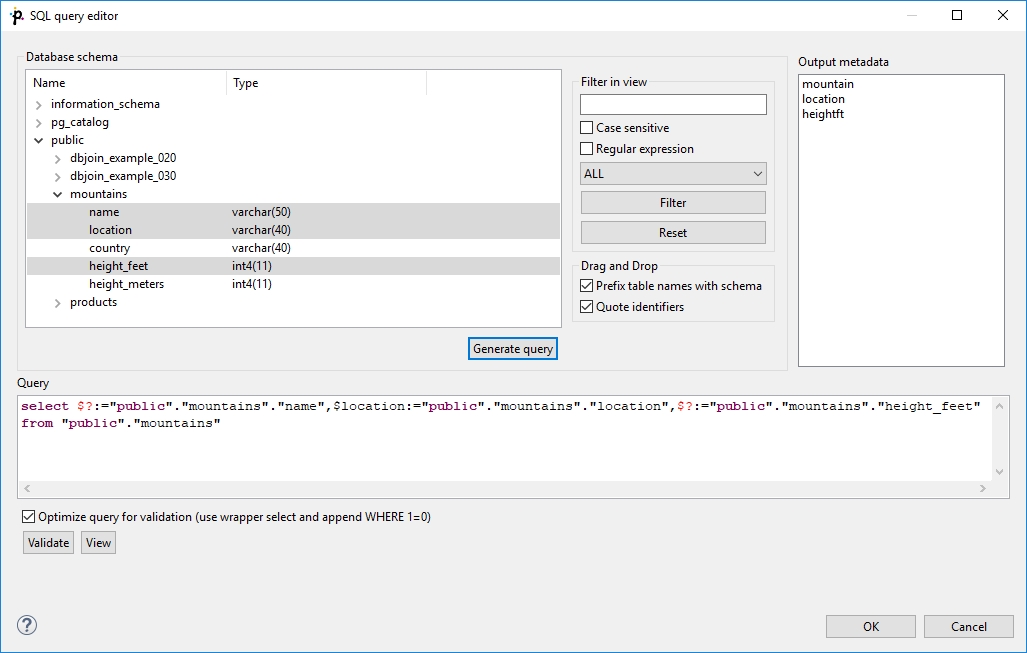
A query may contain question marks if any DB columns differ from output metadata fields. Output metadata are visible in the Output metadata pane on the right side.
Drag and drop the fields from the Output metadata pane to the corresponding places in the Query pane and then manually remove the "$?:=" characters. See the following figure:
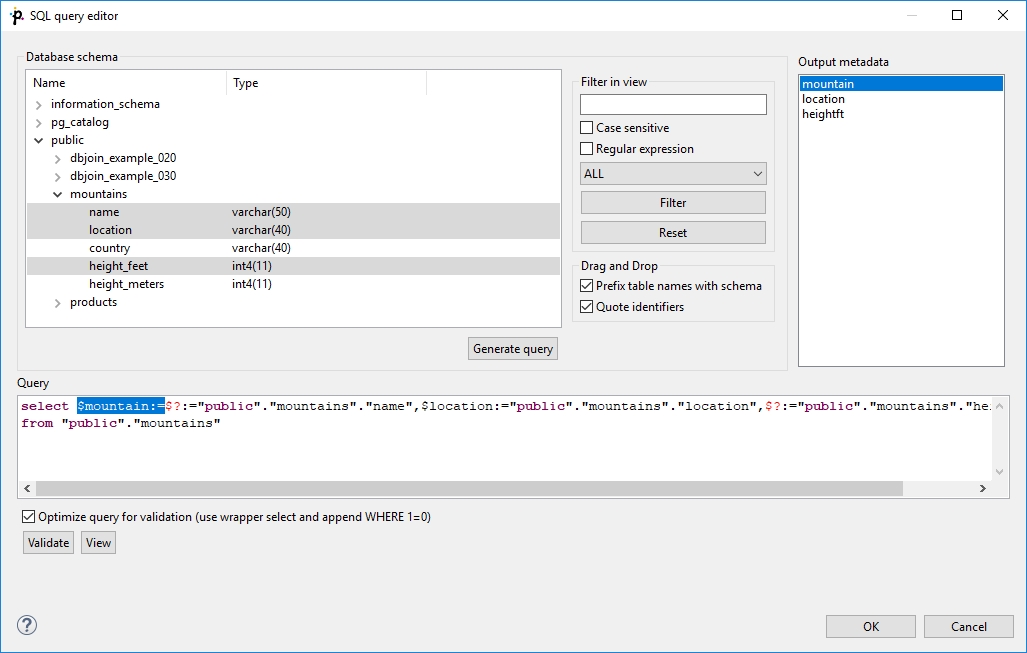
You can also type a where statement to the query.
The buttons underneath allow you to validate the query (Validate) or view data in the table (View).
Examples
Read Records from Database
By generating a query in DatabaseReader, read the name, location and height in feet of mountains from the MountainsDB database.
Solution Use the DB connection and SQL query attributes.
DB connection
See Creating Internal Database Connections.
SQL query
Use the Generate query button in the SQL query editor.
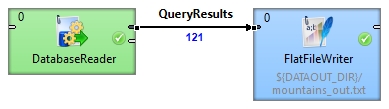
In the output metadata, create the name, location and heightft fields. Set their data types to string, string and integer respectively. Click on the SQL query property and open the SQL query editor. Select the MountainDB database in the Database schema pane. Select the mountain, location and heightft fields and click the Generate query button.
You can validate the generated query and view the results by clicking the respective buttons in the lower left side of the SQL query editor. Set the File URL path of the FlatFileWriter to the external file.
Read Query from Input Port
A query is automatically generated into an external file. Read the query from the file and write the results into another file.
Solution Use the DB connection and Query URL attributes.
DB connection
See Creating Internal Database Connections.
Query URL
port:$0.field1:discrete
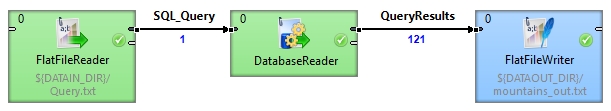
Set the File URL path of the FlatFileReader to the external file containing the query. According to the table above, set the DB connection and Query URL attributes of the DatabaseReader. Set the File URL path of the FlatFileWriter to an external file of your choice. Input metadata should contain one field in which the query will be written. Output metadata should contain a number of fields equivalent to columns selected in the query.
Incremental reading
Incremental Reading allows you to read only new records from a database. This can be done by setting the Incremental key and Incremental file attributes, and editing the Query attribute.
Let us have a database of customers. Each row in the database consists of an id, date, first name and last name, for example:
1|2018-02-01 23:58:02|Rocky|Whitson
2|2018-02-01 23:59:56|Marisa|Callaghan
3|2018-03-01 00:03:12|Yaeko|Gonzale
4|2018-03-01 00:15:41|Jeana|Rabine
5|2018-03-01 00:32:22|Daniele|Hagey
Read the records, then add a new record to the database and run the graph again reading only the new record.
Solution In the output metadata, create the id, date, firstName and lastName fields. Set their data types to integer, date, string and string, respectively. Use the Incremental key and Incremental file attributes.
Incremental key
key01="LAST(id)" ] {
Incremental file
${DATATMP_DIR}/customers_inc_key
[1] Follow the instructions in Incremental Reading to create the Incremental key and edit the Query attribute.
After the first read, the output file contains five records.
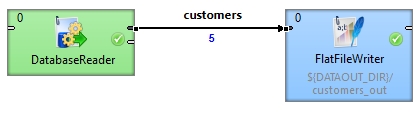
Now, add a new record to the database, for example:
6|2018-03-01 00:51:31|Nathalie|Mangram
and run the graph again.
This time, only the new record is written to the output file, ignoring the previously processed records.
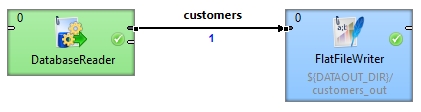
Best Practices
If the Query URL attribute is used, we recommend to explicitly specify Query source charset.
See also
DatabaseWriter DBExecute Common Properties of Components Specific Attribute Types Common Properties of Readers Database Connections
Last updated