HTTPConnector
Short Description
HTTPConnector sends HTTP requests to a web server and receives responses. The request is written in a file or in the graph itself or it is received through a single input port. The response can be sent to an output port, stored to a specified file or stored to a temporary file. The path to the file can then be sent to a specified output port.
HTTPConnector
-
x
0-1
0-2
-
x
x
✓
Ports
Input
0
x
For setting various attributes of the component
Any
Output
0
x
For a response content, response file path, status code, component attributes…
Any
1
x
For error details
Any
Metadata
HTTPConnector does not propagate metadata.
HTTPConnector has metadata templates on its ports available.
You do not have to use metadata templates on input and output edges.
See general details on metadata templates.
Input
1
URL
string
2
requestMethod
string
3
addInputFieldsAsParameters
boolean
4
addInputFieldsAsParametersTo
string
5
ignoredFields
string
6
additionalHTTPHeaderProperties
string
7
charset
string
8
requestContent
string
9
requestContentByte
byte
10
inputFileURL
string
11
outputFileURL
string
12
appendOutput
boolean
13
authenticationMethod
string
14
username
string
15
password
string
16
consumerKey
string
17
consumerSecret
string
18
keyStore
string
19
keyStorePassword
string
20
keyAlias
string
21
keyPassword
string
22
trustStore
string
23
trustStorePassword
string
24
storeResponseToTempFile
boolean
25
temporaryFilePrefix
string
26
multipartEntities
string
27
rawHTTPHeades
string[]
28
oAuth2AccessToken
string
Output
HTTPConnector_Response
1
content
string
The content of the HTTP response as a string. This field will be null, if the response is written to a file.
2
contentByte
byte
The raw content of the HTTP response as an array of bytes. This field will be null, if the response is written to a file.
3
outputFilePath
string
The path to a file, where the response has been written. Will be null, if the response is not written to a file.
4
statusCode
integer
An HTTP status code of the response.
5
header
mapock:parameters]
A map representing HTTP header properties from response.
6
rawHeaders
string[]
7
errorMesage
string
An error message, in case that the error output is redirected to a standard output port.
HTTPConnector_Error
1
errorMessage
string
Error message
HTTPConnector Attributes
Basic
URL
k:p
A URL of the HTTP server the component connects to. May contain one or more placeholders in the following form: *{<field name>}. For the URL format, see Reading of Remote Files. The HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and SFTP protocols are supported. Connecting via a proxy server is available, too, for example: http:(proxy://proxyHost:proxyPort)//
Request method
Method of request.
GET (default) | POST | PUT | PATCH | DELETE | HEAD | OPTIONS | TRACE
Add input fields as parameters
Specifies whether additional parameters from the input edge should be added to the URL. Note: When parameters are read from the input edge and put to the query string, they can contain special characters (?, @, :, etc.). Do not replace such characters with %-notation, HTTPConnector automatically makes them URL-encoded.
false (default) | true
Send parameters in
Specifies whether input fields should be added to the query string or method body. Parameters can only be added to the method body in case that Request method is set to POST.
QUERY (default) | BODY
Ignored fields
Specifies which input fields are not added as parameters. A list of input fields separated by a semicolon is expected.
Additional HTTP headers
Additional properties of the request that will be sent to the Server. A dialog is used to create it, the final form is a sequence of
pairs separated by a comma and the whole sequence is surrounded by curly braces. The value may refer to a field or parameter using a or ${parameterName} notation.
Multipart entities
Specifies fields, that should be added as multipart entities to a POST request. Field name is used as an entity name. A list of input fields separated by a semicolon is expected.
Request/response charset
Character encoding of the input/output files The default encoding depends on DEFAULT_CHARSET_DECODER in defaultProperties
UTF-8 | other encoding
Request content
The request content defined directly in a graph. Can also be specified as the Input file URL or using the requestContent or requestContentByte fields in the Input mapping.
Output file URL
A URL of a file to which an HTTP response is written. See URL file dialog. The output files are not deleted automatically and must be removed manually or as a part of the transformation.
Append output
By default, any new response overwrites the older one. If you switch this attribute to true, the new response is appended to the old ones. Is applied to output files only.
false (default) | true
Input Mapping
Allows to set various properties of the component by mapping their values from an input record.
Output Mapping
Allows to map response data (like a content, status code, etc. ) to the output record. It is also possible to map values from input fields and error details (if Redirect error output is set to true).
Error Mapping
Allows to map an error message to the output record. It is also possible to map values from input fields and attributes.
Redirect error output
Allows to redirect error details to a standard output port.
false (default) | true
Security
Authentication method
Specifies which authentication method should be used.
HTTP BASIC (default) | HTTP DIGEST | ANY
Username
A username required to connect to the server.
Password
A password required to connect to the server.
OAuth1 Consumer key
A consumer key associated with a service. Defines the access token (2-legged OAuth) for signing requests - together with OAuth Consumer secret.
OAuth1 Consumer secret
A consumer secret associated with a service. Defines the access token (2-legged OAuth) for signing requests - together with OAuth Consumer key.
OAuth1 Access Token
An additional field used during OAuth authentication.
OAuth1 Access Token secret
An additional field used during OAuth authentication.
OAuth1 Signature method
Algorithm for signing OAuth message. The HMAC-SHA1 and HMAC-SHA256 methods are supported.
OAuth1 realm
An additional field used during OAuth authentication. Some providers may ignore it.
OAuth2 connection
OAuth2 connection used to obtain access token. No additional configuration is necessary, token will be refreshed automatically when necessary.
Key store
Path to the key store which contains the key pair for client certificate authentication. Leave empty to use the JVM default key store.
Key store password
The password for the Key store.
Key alias
Selects a key from the Key store. If not set, the first key will be used.
Key password
The password for the selected client key. If not set, Key store password is used.
Trust store
Path to the trust store which contains certificates of trusted servers and certification authorities. Leave empty to use the JVM default trust store.
Trust store password
The password for the Trust store.
Disable SSL Certificate Validation
Disables certificate validation of the page you are connecting to. Use this attribute only if you know, what you are doing.
Advanced
Raw HTTP Headers
Additional user-defined HTTP headers defined as text.
e.g. Pragma: no-cache
Request Cookies
Define cookies to be send in an HTTP request. The values of cookies can be set up in Input mapping.
Response Cookies
Define names of response cookies to be used. The mapping can be set up in Output mapping. The names of particular cookies are separated by a semicolon.
E.g. cookie1;cookie2
Store HTTP response to file
k:p
If this attribute is switched to true, a response is written to temporary files with a prefix specified in the Prefix for response names attribute. The path to these temporary files can be retrieved using Output Mapping. Storing a response to temporary files is necessary in case the response body is too large to be stored in a single string data field. The temporary files are deleted automatically after graph finishes (if it has not run in Debug mode).
false (default) | true
Prefix for response files
A prefix that will be used in the name of each output file with an HTTP response. To this prefix, distinguishing numbers are appended.
"http-response-" (default) | other prefix
Stream input file
If the request content is specified by the Input file URL attribute, the input file is uploaded using chunked transfer encoding.
Set the attribute to falseto disable streaming.
true (default) | false
Request parameters
Set up a parameter that has a different name from the field name in the metadata. It enables usage of parameters having names that cannot be used as metadata field names (e.g start-date).
Timeout
How long the component waits to get a response. If it does not receive a response within a specified limit, the execution of the component fails. The HTTPConnector has no timeout by default. Timeout is in milliseconds. Different time units can be used. See Time Intervals
0 (default) | E.g. 5000
Retry Count
How many times should the component retry a request in the case of a failure. Note that the failure does not mean a response status code different from 2xx. A failure is meant same as when component uses error port. Component consider a failure if it cannot process the request/response, i.e. IOException. If it processes the request and gets response with an error status code (e.g. 500), it is not a failure
0 (default)
Retry Delay
How long should the component wait before retrying a request. If the component retries a request it will wait additional time to retrying it. The parameter is list of integers, that are separated by comma. Retry delay is in seconds. If the number of retries is higher than the size of a list, then the last delay in the list is used.
0 (default)
Deprecated
URL from input field
k:p
The name of a stringfield specifying the target URL you wish to retrieve. The field value may contain placeholders in the form *{<field name>}. For the URL format, see Reading of Remote Files. The HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and SFTP protocols are supported.
Input field
k:p
The name of the field of input metadata from which the request content is received. Must be of string data type. May be used for multi HTTP requests.
Output field
The name of the field of output metadata to which the response content is sent. Must be of string data type. May be used for multi HTTP responses.
[1] A URL must be specified by setting one of the URL or URL from field attributes or mapping it in the Input mapping.
[2] The response can be stored either in a file specified in Output file URL or in a temporary file (when Store response file URL to output field is set to true) - it is not possible to use both options.
Details
Input Mapping
Editing the Input mapping attribute opens the Transform Editor where you can decide which component attributes should be set using the input record.
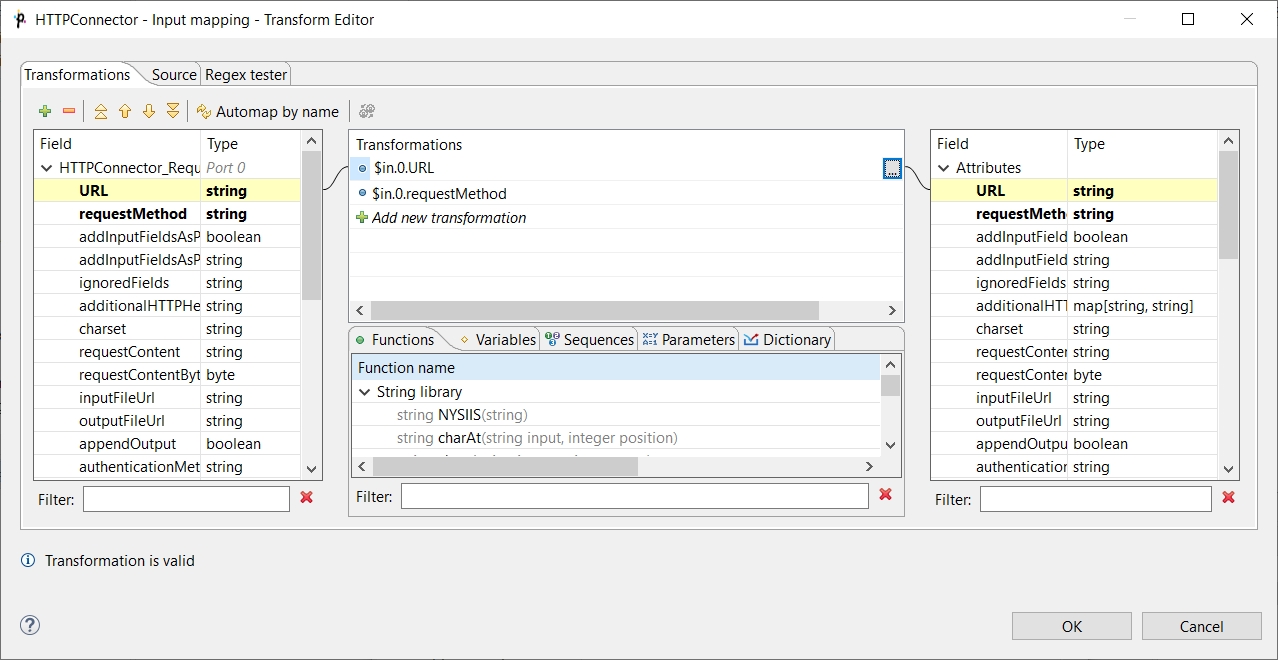
The dialog provides you with all the power and features known from Transform Editor and CTL2 - Data Shaper Transformation Language.
All kinds of CTL functions are available to modify the input field value to be used.
Multipart entities
You can set up multipart entities in the transform editor. Input mapping now offers new fields derived from the value of the Multipart entities attribute. For example, field1;field2 as the value of multipart entities generates the following fields.
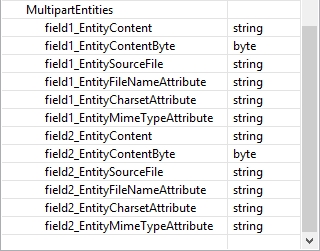
The generated fields can be used to control multipart entities.
If you deal with Multipart entities, you have to use the POST method.
Possible ways of configuration of multipart entities
List of input fields
Compatible with previous versions. The Multipart entities attribute contains a semicolon separated list of fields from the input record. Each field is a multipart entity. The name is same as the field name, the field value is used as a content.
Map content of multipart entity
Use input mapping to set a content of multipart. The multipart name will be same as the fieldname and the content will be specified by a mapping.
Map content and filename
The multipart content will be used by the mapping, but there will be an additional multipart header in the request using the filename as mapped.
Example 47. CTL Mapping and multipart entities
The CTL mapping
function integer transform() {
$out.4.field1_EntityContent="My custom content";
$out.4.field1_EntityFileNameAttribute="MyFilename";
returnALL;
}produces following multipart content.
CB5PZVJDq5RyTWoZqxvtjlbVM0CrMa3Mt
ContentDisposition: formdata; name="field1"; filename="MyFilename"
ContentType: text/plain; charset=UTF8
ContentTransferEncoding: 8bit
My custom content
CB5PZVJDq5RyTWoZqxvtjlbVM0CrMa3MtUse file as multipart entity
To use files as multipart entities, map only the *_File field. Do not map the _Content field.
$out.3.field3_EntitySourceFile = "${PROJECT}/workspace.prm";This will upload the file workspace.prm as a multipart entity.
3xEKe3wUSOl2cRnjwh1UsPVnDOoL7D
ContentDisposition: formdata; name="field3"; filename="workspace.prm"
ContentType: application/octetstream
ContentTransferEncoding: binary
... [here is content of file]
3xEKe3wUSOl2cRnjwh1UsPVnDOoL7DThe file can be specified by a URL similar to the fileURL attribute in readers. But it cannot use the port reading or dictionary reading.
Output Mapping
Editing the attribute opens the Transform Editor where you can decide what should be sent to an output port.
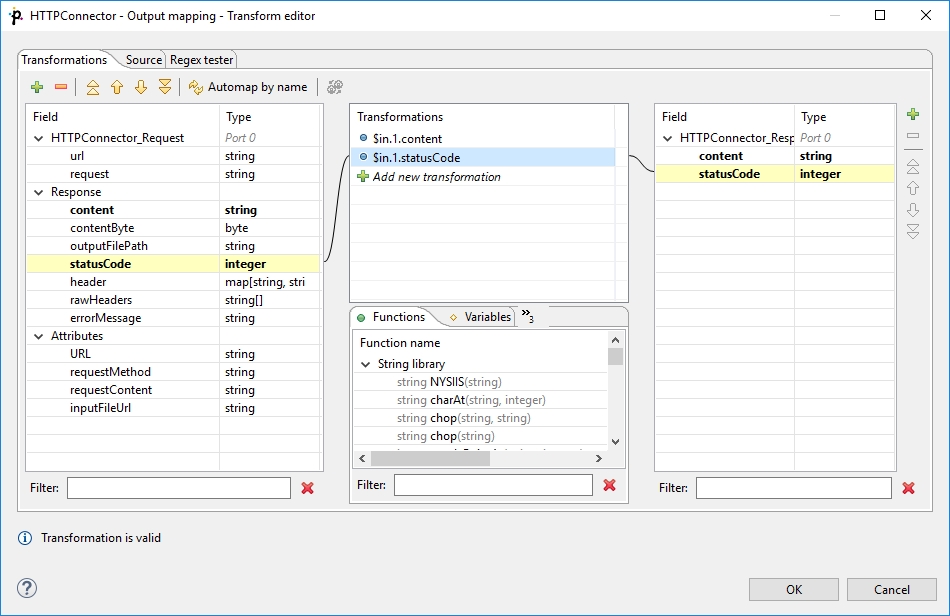
The dialog provides you with all the power and features known from Transform Editor and CTL2 - Data Shaper Transformation Language.
To do the mapping in a few basic steps:
Provided you already have some output metadata, just left-click an item in the left-hand pane and drag it onto an output field. This will send the result data to the output.
If you do not have any output metadata: a. Drag a Field from the left pane and drop it into the right pane (an empty space). b.This produces a new field in the output metadata.
You can map various data to the output port:
Values of fields from input metadata - you can send values from input fields to the output port. This is mainly useful, when you are using some kind of a session identifier for HTTP requests.
Result - provides result data. These includes:
content - the content of the HTTP response as a
string. This field will benullif the response is written to a file.contentByte - the raw content of the HTTP response as an array of bytes. This field will be
nullif the response is written to a file.outputFilePath - the path to a file, where the response has been written. Will be
nullif the response is not written to a file.statusCode - the HTTP status code of the response.
header - the map representing HTTP header properties from the response.
rawHeaders - headers of the response.
errorMessage - the error message in case that the error output is redirected to a standard output port.
Attributes - provides values of the component attributes:
URL - the URL where the request has been sent.
requestMethod - the method that was used for the request.
requestContent - the content of the request, that has been sent (if specified as a string).
inputFileUrl - a URL of the file containing the request content.
Output mapping uses CTL (you can switch to the Source tab). All kinds of functions are available to modify the value to be stored in the output field.
$out.0.prices = find($in.1.content, "price: .*? USD")finds all occurrences of the formprice: [some text] USDin the response content.
If you let output mapping empty, the default output mapping is used:
$out.0.* = $in.0.*;
$out.0.* = $in.1.*;The default mapping has been introduced in version 4.1.0.
Error mapping
Editing the Error mapping attribute opens the Transform Editor where you can map error details to an output port. The behavior is very similar to the Output mapping above.
If you let error mapping empty, the default error mapping is used:
$out.1.* = $in.0.*;
$out.1.* = $in.1.*;The default mapping has been introduced in version 4.1.0.
Notes
When the graph’s log level is set to DEBUG, the HTTPConnector prints the HTTP request and response to graph log.
Examples
Downloading a Web Page
Download the content using HTTPConnector. Save the result to the file for further processing.
Solution
Use the URL and Output file URL attributes. The downloaded page will be saved into the result.html file in the ${DATAOUT_DIR} directory.
Output file URL
${DATAOUT_DIR}/result.html
Downloading Document Requiring HTTP Authentication
Download a document from https://protected.example.org/document.html. The site requires HTTP basic authentication.
Solution
Set up the URL, Output file URL, Username and Password attributes. We suggest to use secure parameters to store your password.
Output file URL
${DATAOUT_DIR}/document.html
Username
myUserName
Password
${PASSWORD}
An alternative solution is to connect an edge to the first output port instead of filling the Output file URL attribute. The result will be send to the edge. No output mapping is necessary.
Connecting via HTTP Proxy without Password
Download the content of the page http://www.primeur.com/. The page is accessible via proxy on 10.0.3.5 listening on TCP port 3128.
Solution
Use the URL attribute. You can use Output file URL to write a result to a file, or connect an output edge.
URL
http:(proxy://10.0.3.5:3128)//www.primeur.com/
Output file URL
${DATAOUT_DIR}/result.html
Connecting via HTTP Proxy using Password
The problem to be solved is similar to the previous example. The difference is that proxy requires a username (test) and password (securePassword).
Solution
URL
http:(proxy://test:[email protected]:3128)//www.primeur.com/
Output file URL
${DATAOUT_DIR}/result.html
Using OAuth in HTTPConnector
Connect to Twitter API and get some tweets about Java.
Solution
Use the URL, OAuth Consumer key, OAuth Consumer secret, OAuth Access Token and OAuth Access Token secret attributes.
Connect an edge to the first output port to pass results by the edge or fill in the Output file URL attribute to write down results to a file.
OAuth Consumer key
yYjLhENks7mNlt7k4l2hKuHXP
OAuth Consumer secret
OE1dkaadjJR8LSOFFlakeH4YRlLkaiqnvVlSlAxZmNlrtoHpyI
OAuth Access Token
3062213700-IJNdsaG3e4vwUasoro4T5p5V2aOxEwYasvrlVs3
OAuth Access Token secret
S2hl7ivynvXI69kzky7Fx3ZJ84ZBCK6vt2G7bW3TFNTO7
Note: The credentials in this example are not valid, you have to use your own credentials.
Upload a File using Multipart Entities
Send a file using multipart entities. The file content is available in field1 field.
Solution
Use the URL, Request method, Multipart entities and Input mapping attributes.
Request method
POST
Add input fields as parameters
true
Multipart entities
field1
Input mapping
See the code below
function integer transform() {
$out.4.field1_EntityContent = $in.0.field1;
return ALL;
}Map multipart entities in the Input mapping dialog.
Using Connection Timeout and Retry Count
Connect to www.my-sometimes-responding-server.com which sometimes fails to respond. The response has to be returned within 20 seconds, otherwise connection should be considered as nonresponding. Make at most 5 attempts in total.
Solution
Use Timeout to set up time limit on connection to avoid waiting if server does not reply. If server responds sometimes only, use Retry count to ask several times.
Timeout is in milliseconds. If you need to set it in seconds, minutes, hours, etc., add the unit. See Time Intervals. Retry count set to 4 causes up to 4 additional retries (if necessary). At most five requests are performed in total.
Best Practices
We recommend users to explicitly specify Request/response charset.
See also
WebServiceClient Common properties of components Specific attribute types
Last updated